Ray Tracing
(Hearn & Baker: p. 527-543. Foley & van Dam: 16.12, p. 776-792 )
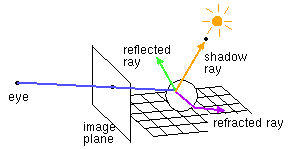
- tuned for specular and transparent objects
- global illumination for specular light
- partly physics-based: geometric optics
Ray tracing tree
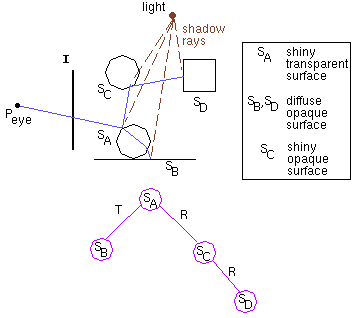
raytrace( ray )
o find closest intersection
o cast shadow ray, calculate colour_local
o colour_reflect = raytrace( reflected_ray )
o colour_refract = raytrace( refracted_ray )
o colour = k1*colour_local + k2*colour_reflect
+ k3*colour_refract
o return( colour )
Comments
- computationally expensive
- avoid intersection calculations
- optimize intersection calculations
- many other optimizations
- antialiasing
- distributed ray tracing
- shadow penumbra
- depth of field
- motion blur
- antialiasing


