


Next: 3.2.6 Piecewise Models
Up: 3.2 Constant Interval Arithmetic
Previous: 3.2.4 Constant Functions
Consider the interval model 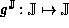 of the function
of the function 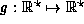 .
The function g has many interval models; we will now define
when the model
.
The function g has many interval models; we will now define
when the model 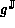 is optimal.
is optimal.
A bound 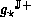 is optimal,
for interval arithmetic, if no better
upper bound exists:
is optimal,
for interval arithmetic, if no better
upper bound exists:
The model 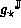 returns optimal upper bounds
if the upper bound is optimal for all
returns optimal upper bounds
if the upper bound is optimal for all 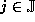 :
:
We may now prove that the interval extension of g
is optimal. Consider the upper bound, for argument j:
from the definition of interval extension.
The only way 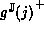 could fail to
be optimal is for there to be a better bound of g(j).
This contradicts the definition of supremum; let the
better bound be denoted as l,
or, equivalently:
but:
could fail to
be optimal is for there to be a better bound of g(j).
This contradicts the definition of supremum; let the
better bound be denoted as l,
or, equivalently:
but:
We now know that if g is differentiable over 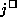 ,
then the upper bound given by
,
then the upper bound given by 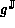 is obtained by
is obtained by 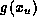 for
some
for
some 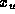 in j:
in j:
since j is closed.
Lower bounds are handled similarly, and will be addressed in section  .
.
Optimality can be defined without direct reference to the underlying function:
It is clear that
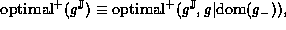 since if
since if 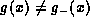 then
then 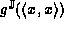 is
clearly not optimal, so
is
clearly not optimal, so 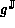 is not optimal.
If
is not optimal.
If 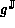 is valid, then
is valid, then 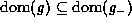 .
.



Next: 3.2.6 Piecewise Models
Up: 3.2 Constant Interval Arithmetic
Previous: 3.2.4 Constant Functions
![]() of the function
of the function ![]() .
The function g has many interval models; we will now define
when the model
.
The function g has many interval models; we will now define
when the model ![]() is optimal.
is optimal.
![]() is optimal,
for interval arithmetic, if no better
upper bound exists:
is optimal,
for interval arithmetic, if no better
upper bound exists:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
then the upper bound given by
,
then the upper bound given by ![]() is obtained by
is obtained by ![]() for
some
for
some ![]() in j:
in j:
![]()
![]()